Blog
A Coding Guide to Implement Zarr for Large-Scale Data: Chunking, Compression, Indexing, and Visualization Techniques
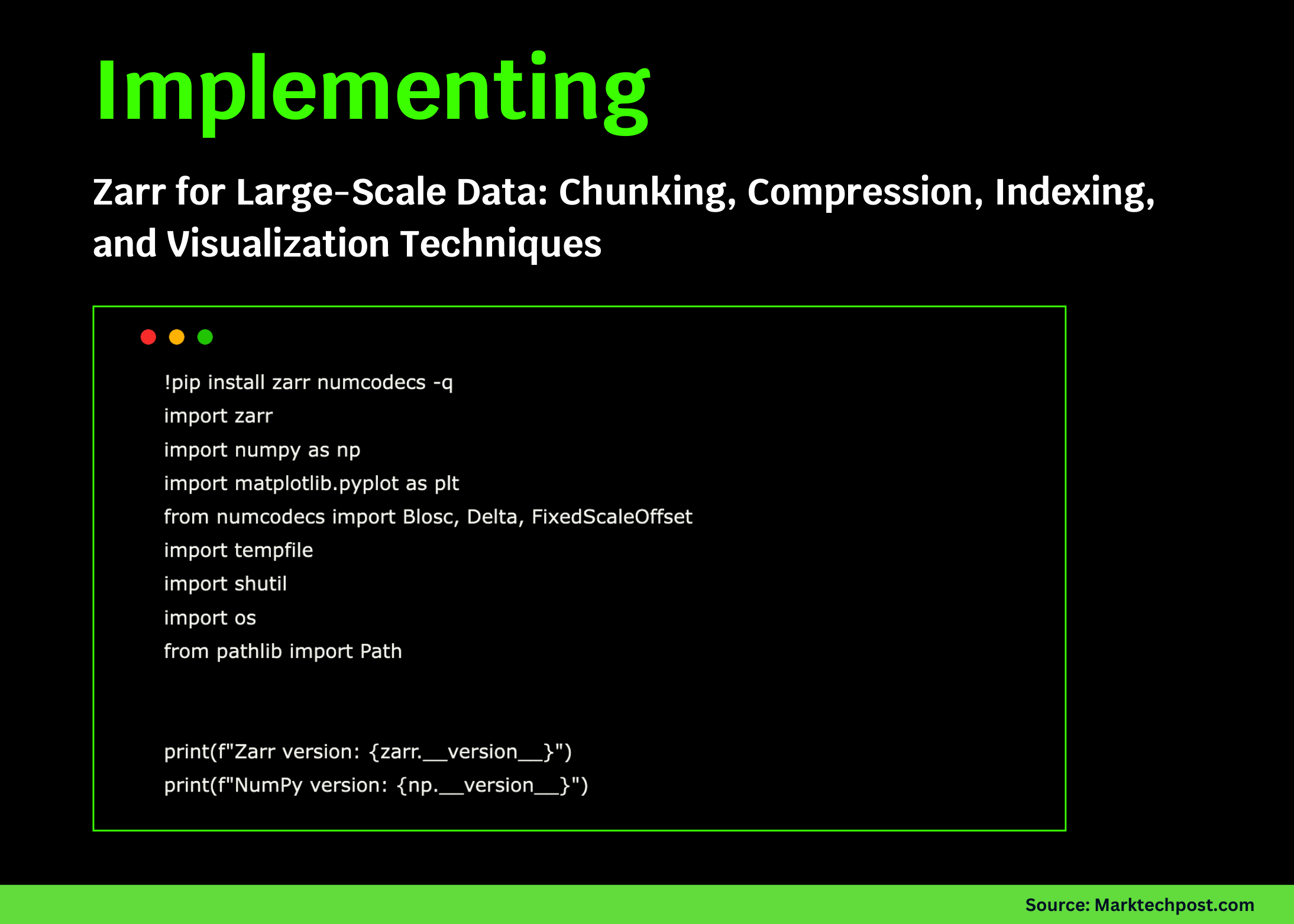
Understanding Zarr for Large-Scale Data Management
Data storage and management have become increasingly crucial in today’s data-driven world. With the rise of big data, effective handling of large datasets is a necessity for organizations. One effective solution to manage extensive datasets is Zarr, a popular format for storing arbitrary-sized chunks of data. This guide will explore the key components of Zarr, focusing on chunking, compression, indexing, and visualization techniques.
What is Zarr?
Zarr is an open-source format designed for the storage of chunked, compressed, and N-dimensional arrays. It is highly suitable for managing large datasets, providing flexibility in how data is accessed and manipulated. The Zarr format is built on the concept of chunking, which divides data into manageable pieces, facilitating efficient storage and retrieval.
Advantages of Using Zarr
- Scalability: Zarr easily scales to handle datasets of varying sizes, making it ideal for small to enormous datasets.
- Flexibility: Users can choose different storage backends—local file systems, cloud storage, or distributed systems.
- Efficiency: With support for chunking and compression, Zarr significantly optimizes both storage space and access speed.
Key Concepts of Zarr
Chunking
Chunking is the process of dividing data into smaller, fixed-size blocks. This technique enhances performance by enabling the retrieval of only the necessary data parts, rather than loading the entire dataset.
Benefits of Chunking:
- Improved Performance: By working with smaller chunks, operations such as file reading and writing become faster and more efficient.
- Memory Management: Chunking allows users to manage memory usage effectively, which is especially important when dealing with large datasets.
- Parallel Processing: Smaller chunks can be processed concurrently, leading to better resource usage and reduced computation time.
To implement chunking in Zarr, you will specify the desired chunk size when creating your dataset. For instance, if you’re working with a 3D array representing an image dataset, you might chunk it based on dimensions relevant to your analyses.
Compression
Compression plays a vital role in data storage, particularly for large datasets where minimizing disk space is a priority. Zarr supports several compression algorithms, including Zlib and Blosc. These algorithms help reduce file sizes, making it easier to manage and transfer data without significant loss of quality.
How to Choose a Compression Method:
- Speed: If rapid data access is a priority, consider faster but less compact algorithms.
- Space: For situations where storage is at a premium, prioritize more effective compression methods, even if they slow down access times.
Implementing compression in your Zarr dataset is as simple as specifying the algorithm and compression level when creating it. For example, using Zlib with a higher compression level will yield smaller file sizes but may take longer to read and write.
Indexing
Indexing enhances the ability to efficiently query and retrieve data from a dataset. Zarr allows users to create indexes that facilitate quicker searches and access patterns, reducing the time taken to locate specific data elements.
Types of Indexing:
- Flat Indexing: Useful for scenarios with simple, hierarchical datasets.
- Multi-dimensional Indexing: Better for complex data structures, such as multi-channel images or time-series data.
To create an index in Zarr, you can define the structure that best fits your data pattern, ensuring faster access times and improved performance.
Best Practices for Implementing Zarr
1. Plan Your Chunk Sizes
When developing a Zarr dataset, plan your chunk sizes carefully. Consider the following factors:
- Dataset Characteristics: Analyze your data to determine optimal chunk dimensions.
- Access Patterns: Understand how frequently you will access data, which helps inform chunk size optimization.
2. Employ Appropriate Compression
Select a compression method suitable for your dataset type. Experiment with different algorithms and settings to find the best balance between speed and storage efficiency.
3. Create Efficient Indexes
Implement indexing structures that reflect your data’s access patterns. This will significantly improve data retrieval speed.
4. Utilize Multi-Backend Capabilities
Zarr supports multiple storage backends. Explore options that best fit your operational requirements, whether it’s local storage, cloud services, or distributed systems.
Visualizing Data with Zarr
Visualization techniques are essential for interpreting data effectively. Integrating visualization into your Zarr workflow allows for a more profound understanding of the underlying data structures.
Steps for Effective Visualization
- Export Data: Begin by exporting relevant data chunks from your Zarr dataset.
- Choose Visualization Libraries: Libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, or Plotly can be utilized for generating plots and charts.
- Create Visual Representations: Use your chosen library to create histograms, scatter plots, or heatmaps that represent the data intuitively.
By following these steps, you can turn complex datasets into easy-to-understand visuals, aiding in data analysis and decision-making.
Conclusion
Zarr is an excellent solution for managing large-scale data through efficient chunking, compression, indexing, and visualization. By implementing best practices, you can optimize your data storage and retrieval processes, ensuring that you adapt to the ever-increasing demands of data analysis and management. As organizations continue to deal with vast amounts of data, mastering Zarr will provide a competitive edge in data-driven environments. Embrace these techniques to unlock the full potential of your datasets.
Elementor Pro
In stock
PixelYourSite Pro
In stock
Rank Math Pro
In stock
Related posts
Building a WordPress Plugin | Jon learns to code with AI
How to add custom Javascript code to WordPress website
6 Best FREE WordPress Contact Form Plugins In 2025!
Solve Puzzles to Silence Alarms and Boost Alertness
Conheça AI do WordPress para construção de sites
WordPress vs Shopify: The Ultimate Comparison for Online Store Owners | Shopify Tutorial
Apple Ends iCloud Support for iOS 10, macOS Sierra on Sept 15, 2025
How to Speed up WordPress Website using AI 🔥(RapidLoad AI Plugin Review)
Bringing AI Agents Into Any UI: The AG-UI Protocol for Real-Time, Structured Agent–Frontend Streams
Web Hosting vs WordPress Web Hosting | The Difference May Break Your Site
Google Lays Off 200+ AI Contractors Amid Unionization Disputes
MIT’s LEGO: A Compiler for AI Chips that Auto-Generates Fast, Efficient Spatial Accelerators
Products
-
 Rayzi : Live streaming, PK Battel, Multi Live, Voice Chat Room, Beauty Filter with Admin Panel
Rayzi : Live streaming, PK Battel, Multi Live, Voice Chat Room, Beauty Filter with Admin Panel
$98.40Original price was: $98.40.$34.44Current price is: $34.44.In stock
-
 Team Showcase – WordPress Plugin
Team Showcase – WordPress Plugin
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 ChatBot for WooCommerce – Retargeting, Exit Intent, Abandoned Cart, Facebook Live Chat – WoowBot
ChatBot for WooCommerce – Retargeting, Exit Intent, Abandoned Cart, Facebook Live Chat – WoowBot
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 FOX – Currency Switcher Professional for WooCommerce
FOX – Currency Switcher Professional for WooCommerce
$41.00Original price was: $41.00.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 WooCommerce Attach Me!
WooCommerce Attach Me!
$41.00Original price was: $41.00.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 Magic Post Thumbnail Pro
Magic Post Thumbnail Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.69Current price is: $3.69.In stock
-
 Bus Ticket Booking with Seat Reservation PRO
Bus Ticket Booking with Seat Reservation PRO
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 GiveWP + Addons
GiveWP + Addons
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.85Current price is: $3.85.In stock
-
 JetBlog – Blogging Package for Elementor Page Builder
JetBlog – Blogging Package for Elementor Page Builder
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 ACF Views Pro
ACF Views Pro
$62.73Original price was: $62.73.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Kadence Theme Pro
Kadence Theme Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.69Current price is: $3.69.In stock
-
 LoginPress Pro
LoginPress Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 ElementsKit – Addons for Elementor
ElementsKit – Addons for Elementor
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.02Current price is: $4.02.In stock
-
 CartBounty Pro – Save and recover abandoned carts for WooCommerce
CartBounty Pro – Save and recover abandoned carts for WooCommerce
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Checkout Field Editor and Manager for WooCommerce Pro
Checkout Field Editor and Manager for WooCommerce Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Social Auto Poster
Social Auto Poster
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Vitepos Pro
Vitepos Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$12.30Current price is: $12.30.In stock
-
 Digits : WordPress Mobile Number Signup and Login
Digits : WordPress Mobile Number Signup and Login
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 JetEngine For Elementor
JetEngine For Elementor
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 BookingPress Pro – Appointment Booking plugin
BookingPress Pro – Appointment Booking plugin
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Polylang Pro
Polylang Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 All-in-One WP Migration Unlimited Extension
All-in-One WP Migration Unlimited Extension
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Slider Revolution Responsive WordPress Plugin
Slider Revolution Responsive WordPress Plugin
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.51Current price is: $4.51.In stock
-
 Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) Pro
Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) Pro
$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$3.94Current price is: $3.94.In stock
-
 Gillion | Multi-Concept Blog/Magazine & Shop WordPress AMP Theme
Rated 4.60 out of 5
Gillion | Multi-Concept Blog/Magazine & Shop WordPress AMP Theme
Rated 4.60 out of 5$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$5.00Current price is: $5.00.In stock
-
 Eidmart | Digital Marketplace WordPress Theme
Rated 4.70 out of 5
Eidmart | Digital Marketplace WordPress Theme
Rated 4.70 out of 5$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$5.00Current price is: $5.00.In stock
-
 Phox - Hosting WordPress & WHMCS Theme
Rated 4.89 out of 5
Phox - Hosting WordPress & WHMCS Theme
Rated 4.89 out of 5$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$5.17Current price is: $5.17.In stock
-
 Cuinare - Multivendor Restaurant WordPress Theme
Rated 4.14 out of 5
Cuinare - Multivendor Restaurant WordPress Theme
Rated 4.14 out of 5$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$5.17Current price is: $5.17.In stock
-
 Eikra - Education WordPress Theme
Rated 4.60 out of 5
Eikra - Education WordPress Theme
Rated 4.60 out of 5$62.73Original price was: $62.73.$5.08Current price is: $5.08.In stock
-
 Tripgo - Tour Booking WordPress Theme
Rated 5.00 out of 5
Tripgo - Tour Booking WordPress Theme
Rated 5.00 out of 5$53.71Original price was: $53.71.$4.76Current price is: $4.76.In stock